The Layers Behind Thermal Transfer Ribbons & Labels
Thermal transfer printing depends on precisely engineered layers within both the ribbon and the label to achieve durable, high-quality prints. Each layer has a specific function, whether it's protecting the printhead, bonding ink to the ribbon, or ensuring that the label adheres securely to various surfaces. Understanding these layers helps businesses choose the right materials for their applications, maximizing print clarity, durability, and longevity. This guide explains the role of each layer in the printing process and highlights how they work together to create effective, long-lasting labels.
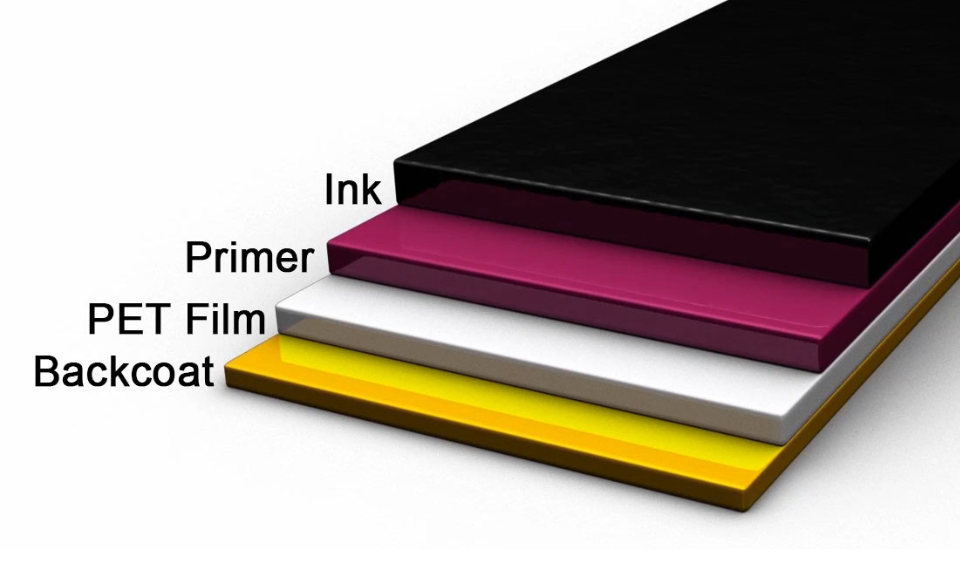
Thermal Transfer Ribbon Layers:
- Backcoat: The backcoat is a protective layer designed to shield the printhead from direct contact with the ribbon. It enhances smooth movement and heat transfer efficiency while prolonging the life of the printhead by reducing wear and friction.
- PET Film: The PET (polyethylene terephthalate) film serves as the carrier layer for the ribbon's other components. As the base layer, it provides a stable foundation onto which the ribbon's ink, primer, and backcoat are applied.
- Primer: The primer layer bonds the ink to the PET film during production. This bonding process improves ink adhesion and transfer to the label, ensuring crisp, durable print results.
- Ink: The ink layer is responsible for creating the printed image. It may consist of wax, resin, or a blend of the two. Wax-based inks are ideal for short-term applications, while resin-based inks offer superior durability, especially for labels exposed to harsh conditions.
Other Components:
- Cores: Ribbons are wound onto either plastic or fiberboard cores. Proper handling and storage of these cores are essential to ensure smooth rewinding and maintain ribbon integrity.
- Leader and Trailer: The leader protects the ribbon during transit and simplifies printer loading. The trailer, located at the ribbon's end, activates the printer's optical sensors, signaling the machine to stop before the ribbon fully runs out, preventing printhead damage.
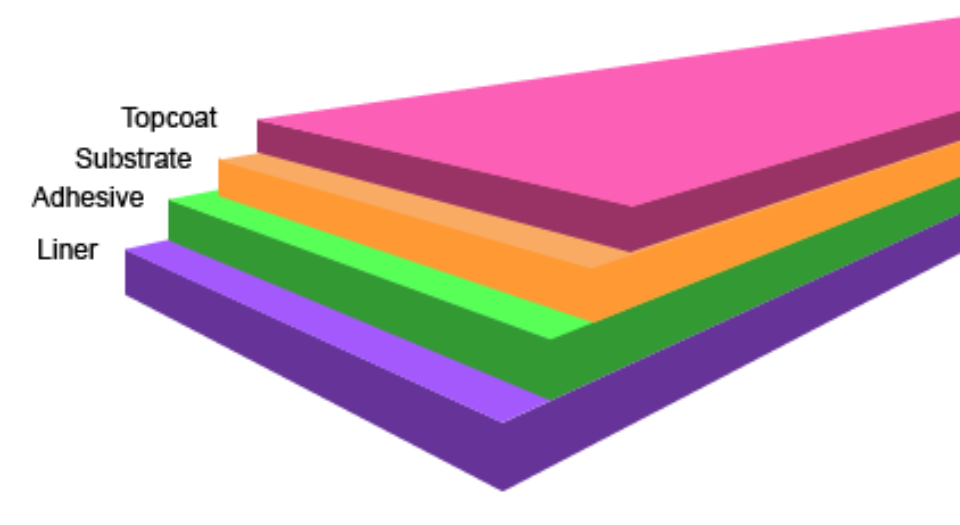
Label Layers for Thermal Transfer Printing:
- Liner: Typically made from silicone-coated paper, the liner supports the label during printing. It safeguards the adhesive layer, ensuring easy handling. The liner is removed at the point of application, leaving only the label and adhesive.
- Adhesive: This layer bonds the label to the desired surface. Adhesives vary by application, with options for permanent or removable bonds. When selecting an adhesive, key considerations include the application surface's texture, environmental factors, and durability needs.
- Substrate: The substrate layer serves as the primary material that receives the printed image. Depending on the application, substrates range from paper for general use to synthetics for increased durability, especially in harsh environments.
- Topcoat: Often used with thermal transfer receptive labels, the topcoat layer enhances ink adhesion, ensuring consistent, high-quality prints. The topcoat may also add durability, making it ideal for applications where the label must resist smudging or wear.